The distribution of continents and oceans refers to the relative position of landmasses and ocean basins. These change over millions of years due to the movement of tectonic plates.
Tectonic plates only move about 2-10 cm per year, but over tens to hundreds of millions of years these slow shifts translate into movements from hundreds to tens of thousands of kilometers, altering the size, shape, and depth of ocean basins and the distribution of land masses on Earth, which change global climate and ecosystems.
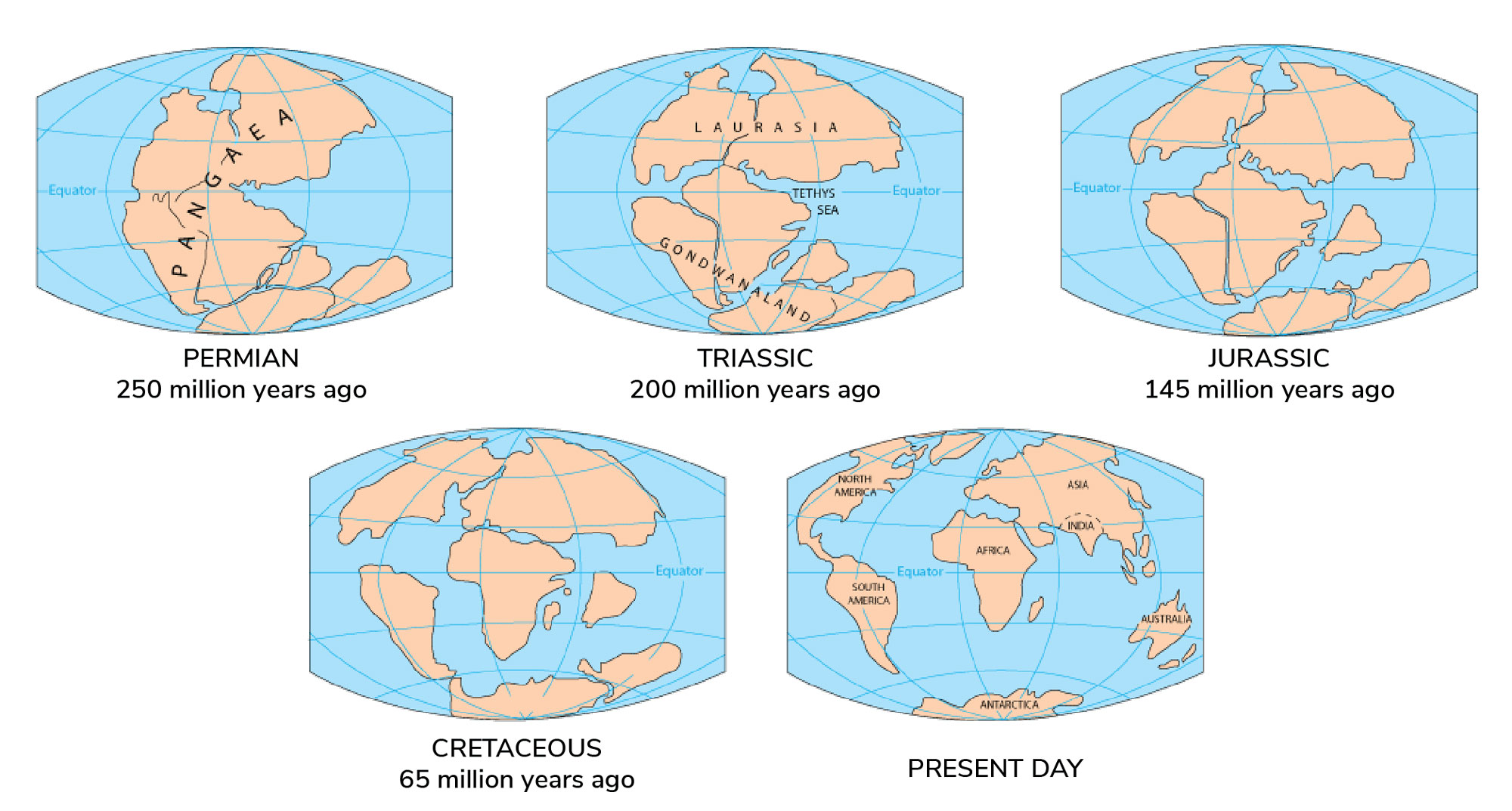
The maps above shows how the distribution of continents and oceans has changed over the last 250 million years. Source: USGS
Changes in the locations of oceans and land masses influences the Earth system, including:
- How sunlight is absorbed or reflected by the surface of the Earth, which in turn affects atmospheric and ocean circulations patterns. which in turn affects weather and climate. For example, water absorbs and re-radiates more heat than land, so the distribution of land masses and oceans is one factor that affects the total heat balance of the Earth, as well as how that heat is distributed.
- Regional temperatures, which can be more extreme at the center of large continents, with higher and lower temperatures than in coastal regions. Coastal climates can be strongly influenced by the re-radiation of heat and moisture from the ocean, and experience more moderate temperatures throughout the seasons.
- The extent of ice sheets, which can expand when continents are located near the poles.
- Connections among ocean basins and the pattern of ocean currents, which transport heat and influence regional climate.
- The location of mountain building, which occurs as tectonic plates collide. Mountains also influence atmospheric circulation patterns that shape regional climate (temperature and precipitation patterns). Changes in atmospheric circulation can also affect ocean circulation patterns. Mountain building can also influence rates of weathering and greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere.
- The amount of volcanic activity, which can increase during times of faster plate motion.
- Sea levels, as the size and depth of ocean basins slowly changes over millions of years.
- Species ranges and how species interact, which can influence evolutionary processes and patterns of biodiversity.
Visit the plate tectonics and Earth’s internal heat pages to learn more about how the distribution of continents and oceans changes over time.
Investigate
Learn more in these real-world examples, and challenge yourself to construct a model that explains the Earth system relationships.
